Civilizations #2: Paleolithic
Table of Contents
The Paleolithic period began from the c. 3mya - c. 10.000mya, marked by the proliferation of ancient humans, the early usage of fire and the use of stones and thin objects as hunting tools.
Species Evolution Brief #
Explains the evolution and spread of the ancestral species of Homo Sapiens that began in Africa (c. 3mya).
Hominini, Australophitecus, Homo #
Hominini is a tribe consisting of the Hominina and Panina, two sub-tribes that had a variety of species during this period, but to date only three species have survived to this day, namely:
- Pan troglodytes / Chimpanzees (Panina)
- Pan paniscus / Bonobo ( Panina)
- Homo Sapiens / Human (Hominina)
But, we’re going to focus on Homo, this genus is the result of the gradual evolution of the genus Australophitecus.
Several species of Australophitecus (c. 3mya) have already shown evidence of the use of stones as hunting tools, but over time they have been extinct and replaced by the evolutionary genus Homo (c. 2mya), including Homo Habilis, Homo Erectus, Homo Heidelbergenesis and other similiar species.
The Spread and Evolution of Homo #
This species of Homo spread from the continent of Africa to the world driven by resource factors and survived, Homo Erectus was a species that pioneered in expansion outside of Africa followed by evolution into Homo Heidelbergenesis, then Neanderthals or Homo Neanderthalensis from Europe and Denisovans from Asia.
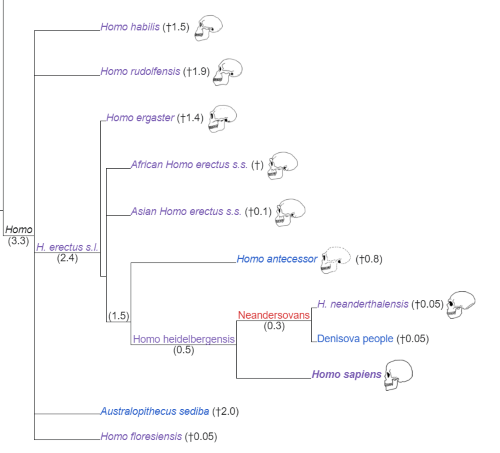
Evolution from species to successive species can occur as a result of adaptation to the environment, lifestyle or intersection of predecessor species.
TL;DR: Because of resource issues, Erectus went out of Africa, evolved into Heidelbergenesis and then evolved to Neanderthals and Denisovans.
Homo Floresiensis #
However, discoveries of Homo Floresiensis in Indonesia indicate that there is a predecessor of Homo Erectus that already emerged from Africa earlier, possibly the species is a precursor or similar to Homo Habilis, of which Homo habilis is the predecesor of the Homo erectus.
This discovery of Homo Floresiensis makes the theory of the spread of ancient humans before Homo Erectus a mystery that scientists have yet to solve.
TL;DR: However, with the discovery of the Floresiensis, we have not yet been able to determine how the migration before the Erectus occurred.
Homo Sapiens #
Among the Homo genus that evolved at that time (c. 2mya - c. 300kya), the species Homo Sapiens (c. 300 - now) was born from the evolution of Homo Heidelbergenesis that exists in Africa.
Bear in mind, that before and after this modern man came, ancient man still existed and they co-existed with these arrivals.

This Homo Sapiens began a further wave of expansion out of Africa, establishing a relatively non-hostile relationship with Neanderthals, Denisovans and other ancient humans.
Sub-Paleolithic Period #
This Paleolithic period is divided into three alternating sub-periods in order:
Lower Paleolithic #
c.3.3mya - c. 300kya, this sub-period is in the epoch geology late pliocene - early pleistocene.
The First Homo Appears #
Australophitecus are at this time, they tend to be frugivorous (memiliki pola makan buah-buahan).
Early appearance of the genus Homo began, the first Homo, Homo Habilis emerged from the evolution of the Australophitecus. Homo habilis are transitioning into carnivorous scavengers through utilizing their primitive stone tools.
The reason they become meat-eaters is that the dryer climate changes make the fruits harder to find and the forests start to turn into savannahs.
Stone tools at this time are in the category Oldowan Industry. The function of this tool is usually used to skining or butchering scavenged animals.
Homo erectus #
c. 1.8mya, the evolution of Homo Habilis, [Homo Erectus] (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Homo_erectus) appeared and began to spread to the corners of the world. Homo Erectus is more sophisticated in every aspects compared to its predecessor. They were the first species to adopt a nomadic lifestyle, a hunter-gatherer, and have more complex socialization.
They’re also the first ancient species to make use a fire.

Homo Erectus also developed their stone tools to be more efficient, i.e. by making them sharper, these stone instruments fall into the Acheulean Industry.
The presence of Homo Erectus is a game changer in the history of ancient mankind, sparking fire, making tools plus nomadic settlement gives them access to more mixed nutrients so that they evolve into species with larger brains for future evolution.
c. 770kya, Homo Erectus evolved into Homo Heidelbergenesis, the ancestor of three species: Homo Sapiens, Homo Neandethalensis and Denisovans.
Middle Paleolithic #
c. 300kya - c. 50kya, this sub-period is in the epoch geological pleistocene.
Modern humans, Homo Sapiens spread all over the world and made cross marriages between Denisovans and Neanderthals as well. They also exchanged knowledge with each other, like Homo sapiens that accommodated the knowledge of making tools from Neandertals.
Neanderthals #
c. 500kya - c. 30kya, Neanderthals often get the stereotype “caveman” by popular media, often described as a primitive, low-intelligence and brute.
In fact, Neanderthals have evidence that they are a skilled species with stone tools that they make with Levallois techniques, these stone instruments fall into the category Mousterian Industry.

Besides, some evidence suggests that Neanderthals once performed symbolic rituals.
Technology #
Significant improvisation has taken place in the manufacture of tools since the Neanderthals invented the Levallois technique, preparing stones of a particular shape before being cut into more specialized tools such as spear-eye, meat-cutting machine or, spear eye.

Trying tree branches as a handle for the stone tool they make, this will make it easier to use the tool and the tool with a more diverse specialization for future production.
Using bones and horns, in addition to rocks, they also use animal bones to make needles, spear eyes, or other tools.
The use of plant fiber and animal skins for clothing is also speculated to begin in this time.
Fire and cooking are also common in this period.
Social interaction #
Homo Sapiens and similar species gradually change their lifestyles to semi-nomads. They live in cave with a group of 10-30 people band that includes one large family or combination of 2-5 other nomadic families.
The gender and labor division has begun to emerge nowadays, men dividing their duties into hunters and guards, women taking care of young children and parents in their homes, some women also foraging for plants with children not far from their homes.

Interaction between species/groups also occurs through proto-language dialogue, knowledge-sharing, coordination or even joint rituals and cultural exchanges.
Overall, their social lives can also be described as “ancient forms of communism”, where they live equitably, hunting results are evenly distributed.
Nutrition #
The intake of individual nutrients at the time was more dominated by hunting and plants/fruit. They also began to eat fish and shellfish.
Before they eat, they cook food on fire first, and they also start keeping meat safe by drying or smoking it for emergencies.
Cannibalism is also common, usually because of food shortages or rituals at the time.
Upper Paleolithic #
c. 50kya - c. 12kya, at this time ice age peak or Last Glacial Maximum occurs.
Ice Age Peak #

Although ice age often refers to Last Glacial Period, but its peak/maximum occurred in the 26kya - 20kya, Earth’s sea level at that time decreased drastically, forming land bridge:
Beringia, in the Bering Strait gives access to the American continent through Alaska.
Sundaland, in the Greater Sunda landmass providing access between Indochina and Indonesia.
Sahul, between Australia and Papua provides access between Australia, and Papua.
Homo Sapiens Survives #
Because of the immune factors of disease, resources, competition and climate, the species of Homo outside the Homo Sapiens like the Neanderthals are extinct.
Technology #
The remaining human species, Homo Sapiens, continued its journey with technological and cultural advances in the late Paleolithic.
The shape of the knife eye, the tip of the spear and other scratch tools undergo improvisation, thinning the thorns and scratching.
Some coastal settlements have even learned simple navigation and used raft to catch fish.
Culture #
At this time, cultural practices and symbols and beliefs are growing very rapidly.
The most commonly found by archaeology is the venus figurine, an engraved figure in the shape of a naked woman. It’s not clear what it means and what it’s useful for, which scientists clearly assume symbolizes fertility and health.

Cave paintings are also found many times, one of the most famous of which is Lascaux, France.
The end of this period #
The Paleolithic ended with the transition from nomadic life to settlement with housing made with clay. Late this period archaeology also found some early humans who managed to domesticate animals, making experimental ceramic containers.
The settlement and settlement marks the end of the Paleolithic and the beginning of the Neolithical or New Stone Age.